EDUCATION AND POSITIONS HELD:
- M.D, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan (1994)
- Resident doctor, Department of Medicine, Taipei Veteran General Hospital, Taiwan (1996-1999)
- Clinical fellow, Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan (1999-2002)
- Ph.D., Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan (2006)
- Attending Physician, Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan (2002-present)
- Assistant Professor, Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan (2007-2010)
- Adjunct Assistant Professor, Institute of Biotechnology in Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan (2007-2010)
- Visiting Scientist, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, U.S.A (2010-2011)
- Associate Professor, Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan (2010-present)
- Adjunct Associate Professor, Institute of Biotechnology in Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan (2010-present)
HONORS:
- Award of Distinguished Thesis, Tien-Te Lee Biomedical Foundation, Taiwan (2008)
- Ta-Yu Wu Memorial Award, National Science Council, Taiwan (2008)
- Dr. Ta-Cheng Tung Memorial Award for Basic Cancer Research, Chinese Oncology Society, Taiwan (2009)
- First prize of Distinguished Thesis, Taipei Veterans General Hospital (2009, 2011)
- Young Scientist Research Award, Tien-Te Lee Biomedical Foundation, Taiwan (2011)
- Award for Junior Research Investigators, Academia Sinica (2011)
RESEARCH INTERESTS:
Pleiotropic functions of EMT regulators during cancer metastasis
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is one of the major mechanisms of cancer metastasis. However, the pleiotropic effects of EMT regulators in additional to the promotion of cellular migration have been investigated limitedly. We recently discover several novel functions of the EMT regulators during head and neck cancer progression. First, we confirm the direct regulation of the stemness-related gene BMI1 by the EMT regulator Twist1. Twist1 and BMI1 are mutually essential in promoting EMT and tumor-initiating capability. Second, we identify the mechanism of Twist1-induced motility through repressing microRNA let-7i and activating RAC1. Third, we show the induction of chromosomal instability by Twist1-BMI1 through upregulating Aurora A expression. In the future, we will keep focusing on the pleiotropic effects of EMT regulators during cancer metastasis and confirm their clinical significance.
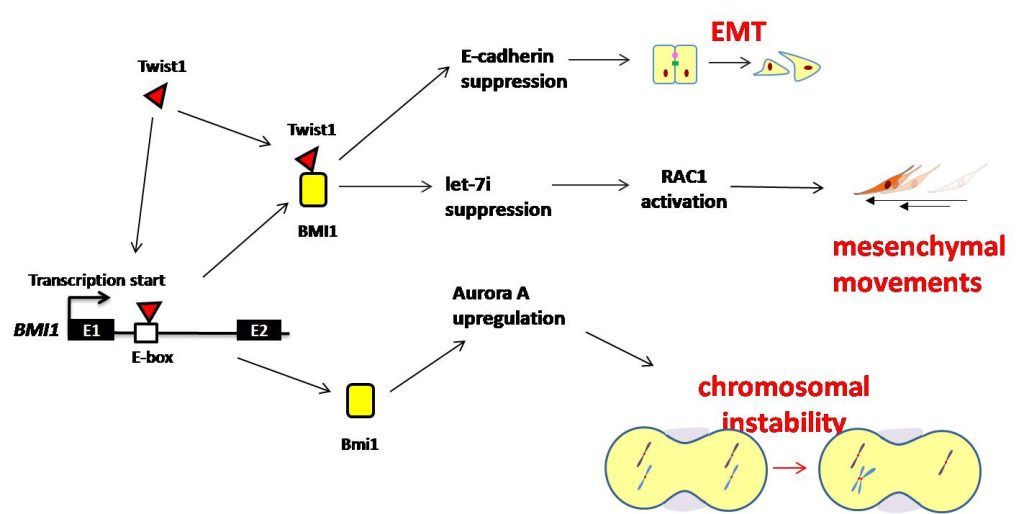
EMT調控因子在腫瘤轉移時的功能多樣性
上皮細胞中胚轉化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)是癌症轉移的主要機制之ㄧ,但產生EMT時,EMT調控因子除促進細胞移動外的多功能性尚未明瞭。我們近年的研究發現在頭頸癌細胞中,EMT調控因子在減低細胞結合及促進移動外,幾項重要的其他功能:Twist1會調控幹細胞基因BMI1並引發幹細胞生成; Twist1藉由抑制微型RNA let-7i表現,引發RAC1活化,使頭頸癌細胞在三維細胞培養系統中產生「間質型運動模式」;Twist1-BMI1會藉由誘發Aurora A 表現,使癌細胞產生染色體不穩定。未來我們將持續專注於癌症轉移時EMT調控因子的功能多樣性之機制研究,並且在臨床上印證其意義。

